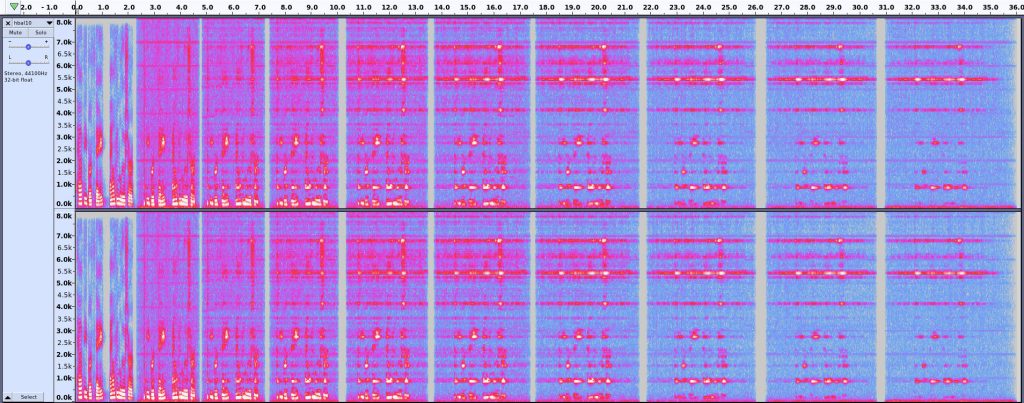
I don’t think I’ve had as much enjoyment for a piece of software for a very long time as I’ve had with BirdNET-Pi. It’s a realtime acoustic bird classification system for the Raspberry Pi. It listens through a microphone you place somewhere near where you can hear birds, and it’ll go off and guess what it’s hearing, using a cut-down version of the BirdNET Sound ID model. It does this 24/7, and saves the samples it hears. You can then go to a web page (running on the same Raspberry Pi) and look up all the species it has heard.
Our Garden
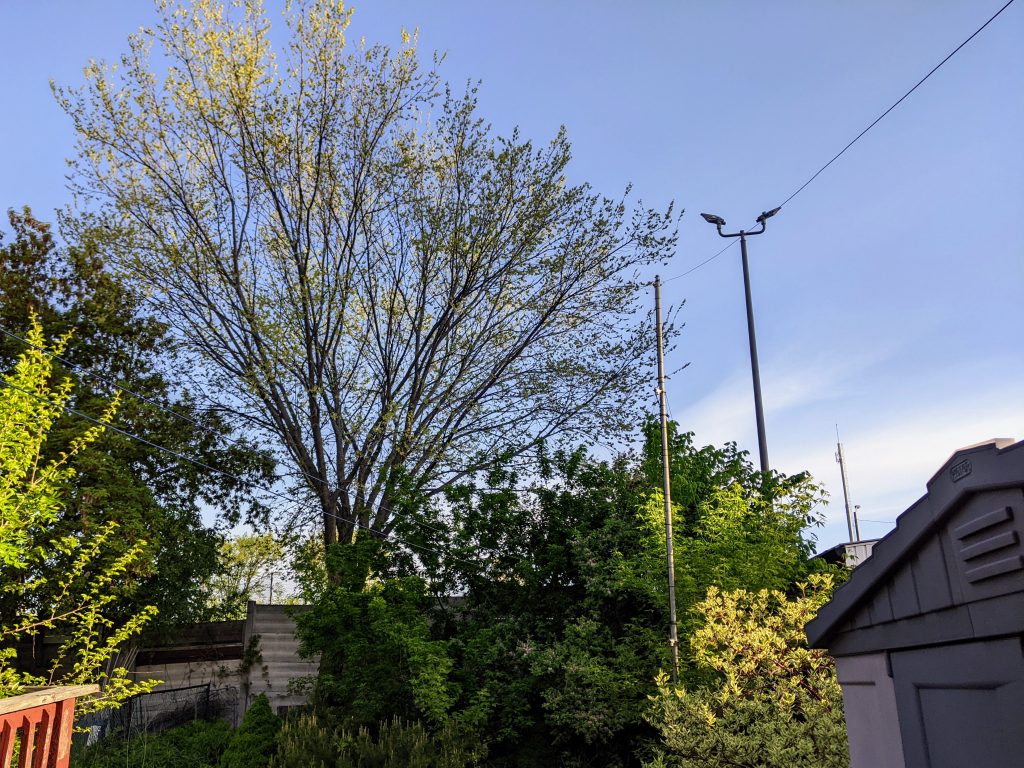

Not very impressive, kind of overgrown, in the wrong part of town. Small, too. But birds love it. At this time of year, it’s alive with birds. You can’t make them out, but there’s a pair of Rose-breasted Grosbeaks happily snacking near the top of the big tree. There are conifers next door too, so we get birds we wouldn’t expect.
We are next to two busy subway/train stations, and in between two schools. There’s a busy intersection nearby, too. Consequently, the background noise is horrendous
What I used
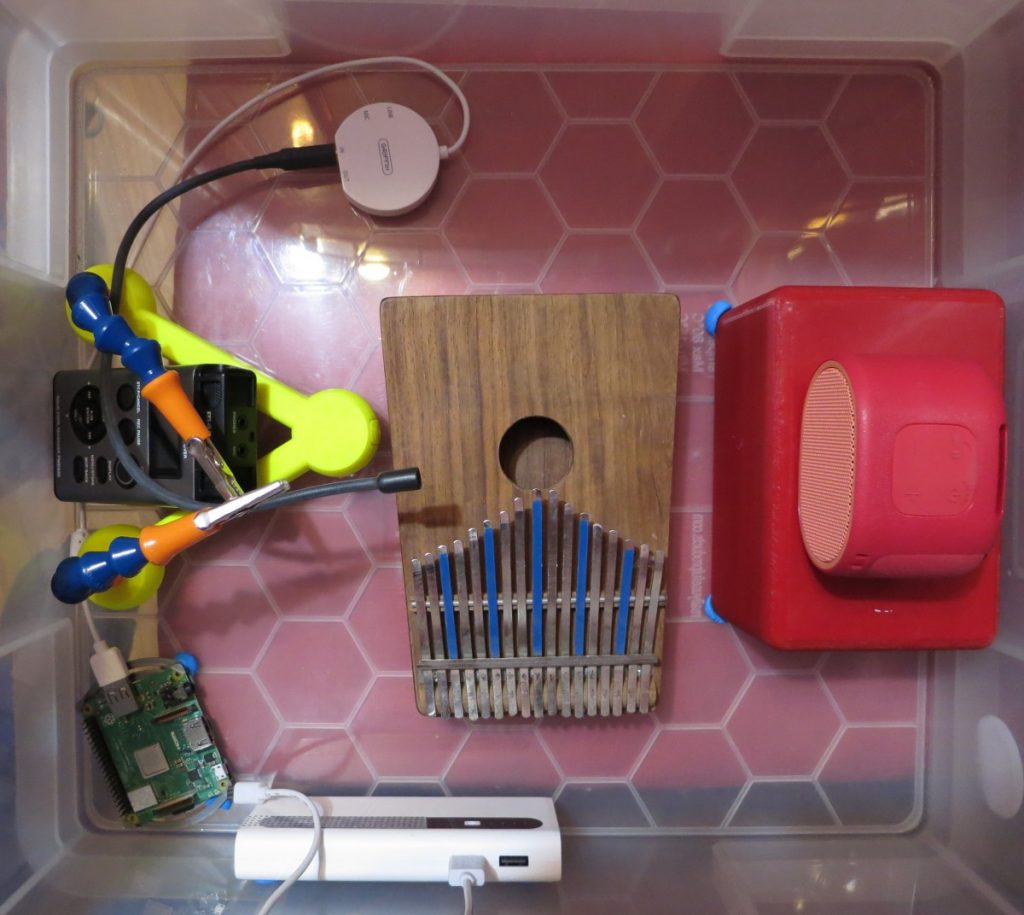
This was literally “stuff I had lying around”:
- Raspberry Pi 3B+ (with power supply, case, thermostatic fan and SD card)
- USB extension cable (this, apparently, is quite important to isolate the USB audio device from electrical noise)
- Horrible cheap USB sound card: I paid about $2 for a “3d sound” thing about a decade ago. It records in mono. It works. My one is wrapped in electrical tape as the case keeps threatening to fall off, plus it has a hugely bright flashing LED the is annoying.
- Desktop mic (circa 2002): before video became a thing, PCs had conferencing microphones. I think I got this one free with a PC over 20 years ago. It’s entirely unremarkable and is not an audiophile device. I stuck it out a back window and used a strip of gaffer tape to stop bugs getting in. It’s not waterproof, but it didn’t rain the whole week it was out the window.
- Raspberry Pi OS Lite 64-bit. Yes, it has to be 64 bit.
- BirdNET-Pi installation on top.
I spent very little time optimizing this. I had to fiddle with microphone gain slightly. That’s all.
What I heard
To the best of my knowledge, I have actual observations of 30 species, observed between May 7th and May 16th 2023:
American Goldfinch, American Robin, Baltimore Oriole, Blue Jay, Cedar Waxwing, Chimney Swift, Clay-colored Sparrow, Common Grackle, Common Raven, Gray Catbird, Hermit Thrush, House Finch, House Sparrow, Killdeer, Mourning Dove, Nashville Warbler, Northern Cardinal, Northern Parula, Orchard Oriole, Ovenbird, Red-winged Blackbird, Ring-billed Gull, Rose-breasted Grosbeak, Ruby-crowned Kinglet, Song Sparrow, Veery, Warbling Vireo, White-throated Sparrow, White-winged Crossbill, Wood Thrush
I’ll put the recordings at the end of this post. Note, though, they’re noisy: Cornell Lab quality they ain’t.
What I learned
This is the first time that I’ve let an “AI” classifier model run with no intervention. If it flags some false positives, then it’s pretty low-stakes when it’s wrong. And how wrong did it get some things!
(This thing stinks out the street, blecch)
There are also false positive for Trumpeter Swans (local dog) and Tundra Swans (kids playing). These samples had recognizable voices, so I didn’t include them here.
The 30 positive species identifications
Many of these have a fairly loud click at the start of the sample, so mind your ears.
American Goldfinch
American Robin
Baltimore Oriole
(I dunno what’s going on here; the next sample’s much more representative)
Blue Jay
Cedar Waxwing
Chimney Swift
Clay-colored Sparrow
Common Grackle
Common Raven
Gray Catbird
Hermit Thrush
House Finch
House Sparrow
Killdeer
Mourning Dove
Nashville Warbler
Northern Cardinal
Hey, we’ve got both of the repetitive songs that these little doozers chirp out all day. Song 1:
and song 2 …
Northern Parula
Orchard Oriole
Ovenbird
Red-winged Blackbird
Ring-billed Gull
Rose-breasted Grosbeak
Ruby-crowned Kinglet
Song Sparrow
Veery
Warbling Vireo
White-throated Sparrow
White-winged Crossbill
Wood Thrush
Boring technical bit
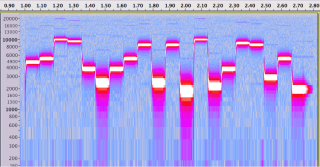
BirdNetPi doesn’t create combined spectrograms with audio as a single video file. What it does do is create an mp3 plus a PNG of the spectrogram. ffmpeg can make a nice not-too-large webm video for sharing:
ffmpeg -loop 1 -y -i 'birb.mp3.png' -i 'birb.mp3' -ac 1 -crf 48 -vf scale=720:-2 -shortest 'birb.webm'(Minor update, May 2024: the original project maintainer has moved on, so I changed the project link to point to Nachtzuster/BirdNET-Pi: A realtime acoustic bird classification system for the Raspberry Pi 5, 4B 3B+ 0W2 and more. Built on the TFLite version of BirdNET.)